1. Take samples across the field, mix them in a bag and send them off to the laboratory for analysis and get back one result for the whole field.
Advantages. Cheap Testing Costs
Disadvantages. Gives a very inaccurate picture for the nutrient status for the different parts of the field where soil types change.
Applications of fertiliser and lime are done using the blanket coverage method ie only one rate across the whole field
Fertiliser and lime can, and are, often applied to areas that don’t have any requirements.
Any variations in rates have to be guessed
2. Take different samples across the field manually, according to where you think the soil type changes and send them off to the Lab
Advantages.
- Better system than above
Cheap testing costs
You have more knowledge of the nutrient requirements for the different soil types.
Manually changing the fertiliser and lime rates can be done
Disadvantages :
- Changing the fertiliser and lime rates has to be done manually.
Changes, could and will be made in the wrong areas especially where the soils can’t be seen ie stubbles and growing crops. Expensive mistakes are likely to be made
3. Take samples using the grid system plotting them with GPS. (this is where the computer places hectare grids over the field and samples are taken in that grid)
Advantages:
Better method than above
Allows for variable rate application maps to be produced
Savings on inputs can be made.
Sampling and mapping can be done in one visit.Disadvantages
- Machinery without GPS cannot use maps
Computer guesstimates where boundaries are for rate changes.
Hot spots can occur where computer gets it wrong.
Variable rates are usually applied by the square blocks.
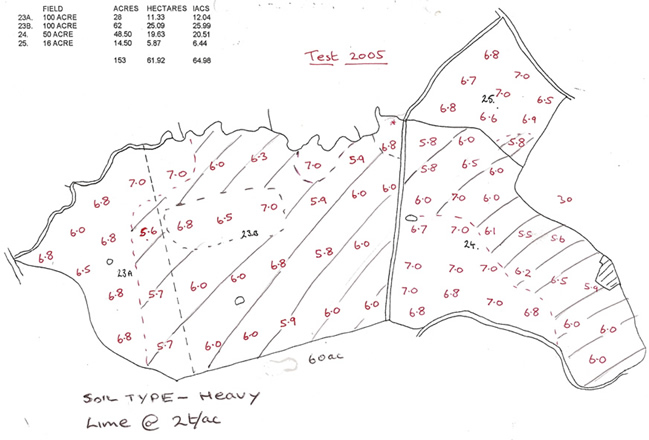
4. The field is scanned with a conductivity meter to produce a detailed soil type map of that field. Each soil type is then sampled individually.
Advantages:
Each soil type is mapped and sampled to produce its own indices
Fertiliser and Lime can be applied precisely to the right places.
Practical maps that a good machinery operator can use even without GPS
Common sense farming.
Most cost effective and accurate way to find out your fertiliser requirements.
The scanning cost is a ‘one off’. Soil types don’t move (well not that quick)
Combine yield maps can be overlaid to see which type is the most productive.
As the scanning only has to be done once. Re-sampling in 4 years time makes this a far cheaper option.Disadvantages:
Needs two visits, (one to scan, one to sample)
- Machinery without GPS cannot use maps
- PH TESTING
